
Selecting a region changes the language and/or content on system image contains a complete snapshot of everything on the computer’s hard drive at any given time. Premiere Pro automatically copies the clip data into the matching XMP properties from that point on. Alternatively, you can use the traditional Clip properties, but turn linking on for all of them. You can use XMP File properties exclusively, so all your metadata is recorded into the source file, visible to other applications. If you never use subclips and never import multiple instances of master clips, then each clip in your project is unique. This option allows applications outside Premiere Pro to access the clip-based metadata by way of the XMP fields. However, in Premiere Pro you can link some clip metadata fields with XMP metadata fields. Only Premiere Pro reads clip instance metadata not, other applications. Clip instance metadata is stored in the Premiere Pro project file, not in the file to which the clip points. Fields under the Clip heading show clip-instance metadata: information about a clip selected in the Project panel, or in a sequence. The Metadata panel shows both clip-instance metadata and XMP file metadata for a selected asset. Using the Source Monitor and Program Monitor.Troubleshoot issues related to playback and performance in Premiere Pro.How do I manage the Media Cache in Premiere Pro?.
 Green and pink video in Premiere Pro or Premiere Rush. Check if your system is compatible with Premiere Pro. Improving Performance and Troubleshooting. Best Practices: Working with native formats. Best Practices: Learning from broadcast production. Consolidate, transcode, and archive projects. Archive, restore, or delete Team Projects. Share and manage changes with Team Project collaborators. Best Practices: Working with Productions. How clips work across projects in a Production. Use Frame.io with Premiere Pro and After Effects. Collaboration: Frame.io, Productions, and Team Projects. Exporting projects for other applications. Exporting for the Web and mobile devices. Using HSL Secondary controls in the Lumetri Color panel. Adjust color using RGB and Hue Saturation Curves. Get creative with color using Lumetri looks. Overview: Color workflows in Premiere Pro. Compositing, alpha channels, and adjusting clip opacity. Viewing and adjusting effects and keyframes. Use Motion effect to edit and animate clips. Adding, navigating, and setting keyframes. Upgrade Legacy titles to Source Graphics. Retiring the Legacy Titler in Premiere Pro | FAQ. Best Practices: Faster graphics workflows. Use data-driven Motion Graphics templates. Replace images or videos in Motion Graphics templates. Install and use Motion Graphics templates. Add Responsive Design features to your graphics. Overview of the Essential Graphics panel. Automatically reframe video for different social media channels. Overview of video effects and transitions. Set up and use Head Mounted Display for immersive video in Premiere Pro. Measure audio using the Loudness Radar effect. Advanced Audio - Submixes, downmixing, and routing. Monitor clip volume and pan using Audio Clip Mixer. Edit, repair, and improve audio using Essential Sound panel.
Green and pink video in Premiere Pro or Premiere Rush. Check if your system is compatible with Premiere Pro. Improving Performance and Troubleshooting. Best Practices: Working with native formats. Best Practices: Learning from broadcast production. Consolidate, transcode, and archive projects. Archive, restore, or delete Team Projects. Share and manage changes with Team Project collaborators. Best Practices: Working with Productions. How clips work across projects in a Production. Use Frame.io with Premiere Pro and After Effects. Collaboration: Frame.io, Productions, and Team Projects. Exporting projects for other applications. Exporting for the Web and mobile devices. Using HSL Secondary controls in the Lumetri Color panel. Adjust color using RGB and Hue Saturation Curves. Get creative with color using Lumetri looks. Overview: Color workflows in Premiere Pro. Compositing, alpha channels, and adjusting clip opacity. Viewing and adjusting effects and keyframes. Use Motion effect to edit and animate clips. Adding, navigating, and setting keyframes. Upgrade Legacy titles to Source Graphics. Retiring the Legacy Titler in Premiere Pro | FAQ. Best Practices: Faster graphics workflows. Use data-driven Motion Graphics templates. Replace images or videos in Motion Graphics templates. Install and use Motion Graphics templates. Add Responsive Design features to your graphics. Overview of the Essential Graphics panel. Automatically reframe video for different social media channels. Overview of video effects and transitions. Set up and use Head Mounted Display for immersive video in Premiere Pro. Measure audio using the Loudness Radar effect. Advanced Audio - Submixes, downmixing, and routing. Monitor clip volume and pan using Audio Clip Mixer. Edit, repair, and improve audio using Essential Sound panel. 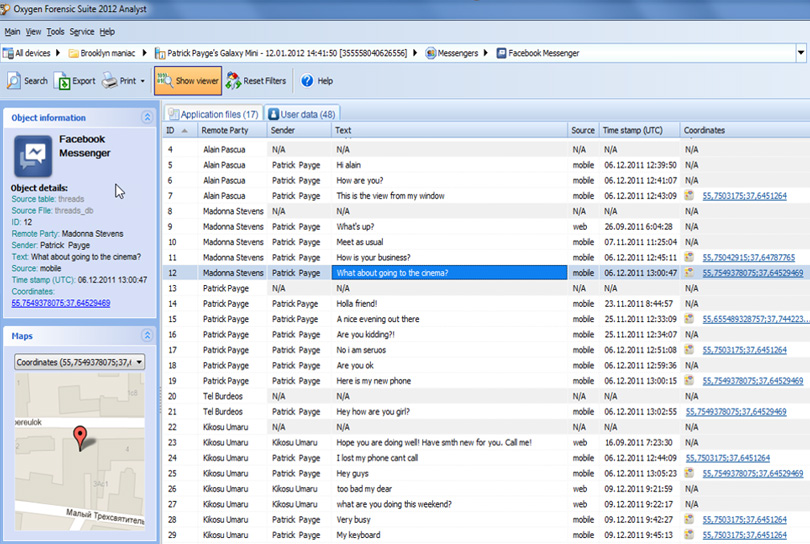 Synchronizing audio and video with Merge Clips.
Synchronizing audio and video with Merge Clips.  Edit from sequences loaded into the Source Monitor. Find, select, and group clips in a sequence. Importing XML project files from Final Cut Pro 7 and Final Cut Pro X. Importing AAF project files from Avid Media Composer. Setting up your system for HD, DV, or HDV capture. Use Premiere Pro in a dual-monitor setup. FAQ | Import and export in Premiere Pro. Best Practices: Create your own project templates. Open and edit Premiere Rush projects in Premiere Pro. Backward compatibility of Premiere Pro projects.
Edit from sequences loaded into the Source Monitor. Find, select, and group clips in a sequence. Importing XML project files from Final Cut Pro 7 and Final Cut Pro X. Importing AAF project files from Avid Media Composer. Setting up your system for HD, DV, or HDV capture. Use Premiere Pro in a dual-monitor setup. FAQ | Import and export in Premiere Pro. Best Practices: Create your own project templates. Open and edit Premiere Rush projects in Premiere Pro. Backward compatibility of Premiere Pro projects. 
GPU Accelerated Rendering & Hardware Encoding/Decoding.Hardware and operating system requirements.








 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
